# React从入门到精通
# React入门
# React简介
用于构建用户界面的Js库(只关注视图),采用声明式编码,组件化编码,React Native编写原生应用。采用虚拟DOM技术和Diffing算法,最小化页面重绘。
# 基本使用
相关js库
- react.js:react核心库
- react-dom.js:提供操作DOM的react扩展库
- babel.min.js:解析JSX语法代码转为JS代码的库
创建虚拟DOM两种方式:
// js方式
const VDOM = React.createElement('h1', { id: 'title' }, 'Hello,React');
// jsx方式
const VDOM = <h1 id="title">Hello,React</h1>;
// jsx方式创建嵌套结构,可以用()包裹作为一个整体
const VDOM = (
<h1 id="title">
<span>Hello,React</span>
</h1>
);
# JSX
基本语法规则:
- 定义虚拟DOM时,不要写引号
- 标签中混入Jsx表达式要用{}
- 样式的类名指定不要用class,要用className
- 内联样式,要用{{}}的形式去写
- 虚拟DOM必须只有一个根标签
- 标签必须闭合
- 标签首字母
- 若小写字母开头,则将改标签转为html同名元素,若html中无该标签对应的同名元素,则标错
- 若大写字母开头,react就渲染对应的组件,若组件没有定义,则标错
注意:
- JSX的设计初衷就是便于创建虚拟DOM,是原始创建虚拟DOM的语法糖
- JSX的{}中只能写js表达式(表达式会产生一个值),不能写for,if等js语句
const data = ["Angular", "React", "Vue"]
// 1. 创建虚拟DOM
const VDOM = (
<div>
<h1>前端JS框架列表</h1>
<ul>
{
data.map((item, index) => {
return <li key={index}>{item}</li>
})
}
</ul>
</div>
)
# 虚拟DOM
- 虚拟DOM就是个普通的Object对象
- 虚拟DOM比较“轻”,真实DOM比较“重”,虚拟DOM在React内部使用,无需真实DOM上的那么多属性
- 虚拟DOM最终会被转化为真实DOM
# React面向组件编程
# 组件的定义方式
# 函数式组件
// 1.创建组件
function MyComponent() {
console.log(this) // 此处的this是undefined,因为babel编译后开启了严格模式
return <h1>函数式组件</h1>
}
// 2.渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.getElementById("test"))
/*
执行了ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />...之后,发生了什么?
1. React解析组件标签,找到了MyComponent组件
2. 发现组件是函数定义的,随后调用该函数,将函数返回的虚拟DOM解析为真实DOM,呈现在页面上
*/
# 类式组件
// 1.类式组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
// render放在MyComponent类的原型对象上,供实例使用
render() {
return <h2>类式组件</h2>
}
}
// 2.渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.getElementById("test"))
/*
执行了ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />...之后,发生了什么?
1. React解析组件标签,找到了MyComponent组件
2. 发现组件是类定义的,随后实例化该类,并通过该实例调用原型上的render的方法,
将函数返回的虚拟DOM解析为真实DOM,呈现在页面上
*/
# 组件三大核心属性:state
- state是组件对象最重要的属性,值是对象(可以包含多个key-value的组合)
- 组件被称为状态机,通过更新组件的state来更新对应的页面显示
# state的引入
class Weather extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
isHot: true
}
}
render() {
return <h1>今天天气很{this.state.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}</h1>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Weather />, document.getElementById("test"))
# state的标准使用
class Weather extends React.Component {
// 构造器调用几次? —— 1次
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 初始化状态
this.state = {
isHot: true,
wind: "微风"
}
// 解决this指向问题
this.changeWeather = this.changeWeather.bind(this)
}
// render调用几次? ———— 1+n次 1是初始化的那次,n是状态更新的次数?
render() {
console.log("render");
const { isHot, wind } = this.state
return (
<h1 onClick={this.changeWeather}>今天天气很{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'},{wind}</h1>
)
}
// changeWeather 调用几次? ———— 点几次 调几次
changeWeather() {
// changeWeather放在Weather的原型对象上,供实例使用
// 这里的changeWeather作为onClick的回调,不是通过实例调用的,类中的方法默认开启局部严格模式
// 所以changeWeather中的this是undefined
// 严重注意:状态state不可直接更改,要借助一个内置api更改
// this.state.isHot = !isHot //错误写法
// 获取原来的isHot
const isHot = this.state.isHot
// 状态必须通过setState来更改,且更新是一种合并,不是替换
this.setState({ isHot: !isHot })
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Weather />, document.getElementById("test"))
# state的简化使用
class Weather extends React.Component {
// 初始化状态
state = {
isHot: true,
wind: "微风"
}
render() {
const { isHot, wind } = this.state
return <h1 onClick={this.changeWeather}>今天天气很{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'},{wind}</h1>
}
// 自定义方法 ———— 要用赋值语句的形式+箭头函数
changeWeather = () => {
const isHot = this.state.isHot
this.setState({ isHot: !isHot })
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Weather />, document.getElementById("test"))
注意:
- 组件中的render方法中的this为组件的实例对象
- 组件自定义方法中的this为undefined,如何解决?
- 强制绑定this,通过函数对象的bind()
- 箭头函数
- 状态数据,不能直接修改或更新
# 组件三大核心属性:props
props作用:
- 通过标签属性从组件外向组件内传递变化的数据
- 注意:组件内部不要修改props数据
# props基本使用
// 创建组件
class Person extends React.Component {
render() {
const { name, age, sex } = this.props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>性别:{sex}</li>
<li>年龄: {age}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
// 使用属性名
ReactDOM.render(<Person name="tom" age="18" sex="女" />, document.getElementById("test1"))
// 批量传递
const p = { name: "老刘", age: 18, sex: "男" }
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p} />, document.getElementById("test1"))
# 对props进行限制
(React15.5之后PropTypes不再存在于React对象)
// 对props进行限制
Person.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired, // 限制name为字符串,且必传
sex: PropTypes.string, // 限制sex为字符串
age: PropTypes.number.isRequired, // 限制age为数字,且必传
speak: PropTypes.func, // 限制speak为函数
}
// props默认值
Person.defaultProps = {
sex: '男', // sex默认值为男
age: 18 // age默认值为18
}
简写方式
class Person extends React.Component {
// 对props进行限制
static propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired, // 限制name为字符串,且必传
sex: PropTypes.string, // 限制sex为字符串
age: PropTypes.number.isRequired, // 限制age为数字,且必传
speak: PropTypes.func // 限制speak为函数
}
// props默认值
static defaultProps = {
sex: '男', // sex默认值为男
age: 18 // age默认值为18
}
}
注:最好写在类里面
补充说明:尽量不要在类组件写构造器
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 如果需要在构造器里面使用this.props, 那么必须接受props并且通过super传递props
console.log(this.props)
}
# 函数式组件使用props
function Person(props) {
const { name, age, sex } = props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>性别:{sex}</li>
<li>年龄: {age + 1}</li>
</ul>
)
}
// 对props进行限制
Person.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired, // 限制name为字符串,且必传
sex: PropTypes.string, // 限制sex为字符串
age: PropTypes.number.isRequired, // 限制age为数字,且必传
speak: PropTypes.func // 限制speak为函数
}
// props默认值
Person.defaultProps = {
sex: '女', // sex默认值为男
age: 18 // age默认值为18
}
ReactDOM.render(<Person name="jerry" age={19} sex="男" />, document.getElementById("test3"))
注:函数没有自身的this,可以使用props,props从函数的参数中获取,不能使用state和refs
# 组件三大核心属性:refs与事件处理
作用:
- 组件内的标签可以定义
ref来标识自己, - react会收集带有ref属性的标签到
refs属性中
# 字符串形式的ref
class Demo extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref="input1" type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据" />
<button ref="button1" onClick={this.showData}>点我提示左侧数据</button>
<input ref="input2" onBlur={this.showData2} type="text" placeholder="失去焦点提示数据" />
</div>
)
}
showData = () => {
const { input1 } = this.refs
console.log(input1.value)
}
showData2 = () => {
const { input2 } = this.refs
console.log(input2.value)
}
}
注:字符串ref效率不高,
不推荐使用
# 回调函数形式的ref
通过箭头回调函数,将当前标签挂载到实例自身上
class Demo extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref={c => this.input1 = c} type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据" />
<button onClick={this.showData}>点我提示左侧数据</button>
<input ref={c => this.input2 = c} onBlur={this.showData2} type="text" placeholder="失去焦点提示数据" />
</div>
)
}
showData = () => {
console.log(this.input1.value)
}
showData2 = () => {
console.log(this.input2.value)
}
}
回调ref调用次数的问题?
render() {
const { isHot } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2>今天天气很{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}</h2>
<input ref={this.saveInput} type="text" />
<button onClick={this.showInfo}>点我提示输入的数据</button>
<button onClick={this.changeWeather}>点我切换天气</button>
</div>
)
}
saveInput = (c) => {
this.input1 = c
console.log('@', c)
}
注意:
- 回调函数形式的ref,在更新的时候会
执行两次,先清除旧的,再创建新的- 改为类绑定函数的形式可以
避免调用两次
# createRef创建ref容器
class Demo extends React.Component {
// React.createRef()创建一个容器,该容器可以存储被ref标识的节点
myRef = React.createRef()
myRef2 = React.createRef()
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref={this.myRef} type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据" />
<button onClick={this.showData}>点我提示左侧数据</button>
<input onBlur={this.showData2} ref={this.myRef2} type="text" placeholder="失去焦点提示数据" />
</div>
)
}
showData = () => {
// 通过current获取当前绑定节点
console.log(this.myRef.current)
}
showData2 = () => {
console.log(this.myRef2.current.value)
}
}
注:
官方推荐方式
# 事件处理
- React通过onXxx属性指定事件处理函数(注意大小写)
- React使用自定义事件,而不是原生DOM事件,——为了更好的兼容性
- React中的事件是通过
事件委托方式处理的,委托给组件最外层元素,——为了高效
- 通过event.target得到事件发生事件DOM元素对象,——不要过度使用ref
注:当发生事件的元素正好是需要操作的元素的时候,可以
省略ref
# 收集表单数据
- 受控组件:页面表单数据变化后,维护在state里,需要的时候从state中取
- 非受控组件:页面表单数据,现用现取
# 高阶函数与函数柯里化
高阶函数:如果一个函数接受的参数是一个函数,或者返回值是一个函数,那么称这个函数为高阶函数。常见的高阶函数:Promise、setTimeOut、arr.map()、...
函数的柯里化:通过函数调用继续返回函数的形式,实现多次接收参数最后统一处理的函数编码形式
// 表单数据保存到状态中
saveFormData = (dataType) => {
return (e) => {
this.setState({ [dataType]: e.target.value })
}
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
用户名:<input onChange={this.saveFormData('username')} type="text" name="username" />
密码:<input onChange={this.saveFormData('password')} type="password" name="password" />
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
- 不用柯里化的写法
// 表单数据保存到状态中
saveFormData = (dataType, e) => {
this.setState({ [dataType]: e.target.value })
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
用户名:<input onChange={(e) => { this.saveFormData('username', e) }} type="text" name="username" />
密码:<input onChange={(e) => { this.saveFormData('password', e) }} type="password" name="password" />
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
# 组件生命周期
# 引入生命周期
// 创建组件
class Life extends React.Component {
state = {
opacity: 1
}
death = () => {
// 卸载组件
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById("test"))
}
// 组件挂载完毕
componentDidMount() {
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
// 获取原状态
let { opacity } = this.state
opacity -= 0.05
if (opacity <= 0) opacity = 1
this.setState({ opacity })
}, 100)
}
// 组件将要被卸载
componentWillUnmount() {
// 清除定时器
clearInterval(this.timer)
}
// render调用的时机:初始化渲染,状态更新之后
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2 style={{ opacity: this.state.opacity }}>React学不会怎么办?</h2>
<button onClick={this.death}>不活了</button>
</div>
)
}
}
# 生命周期流程图(旧)
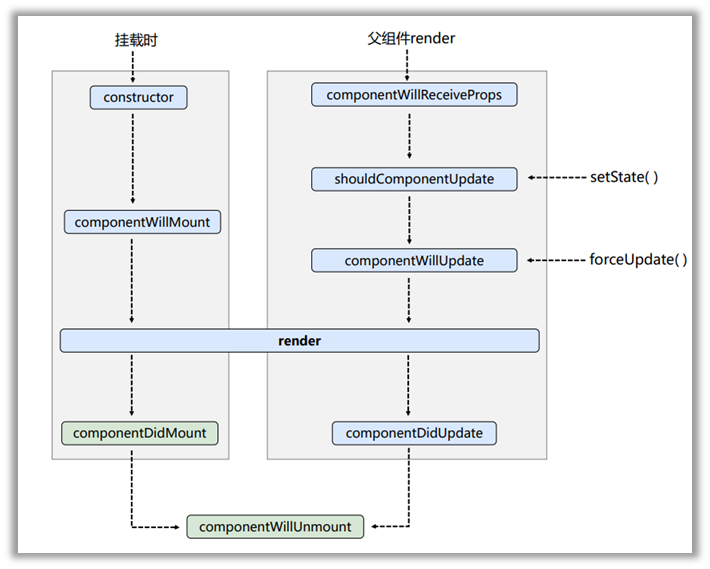
1、组件挂载生命周期
// 创建组件
class Count extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
console.log("Count---constructor");
super(props)
this.state = { count: 0 }
}
add = () => {
const { count } = this.state
this.setState({ count: count + 1 })
}
death = () => {
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById("test"))
}
force = () => {
this.forceUpdate()
}
// 组件将要挂载
componentWillMount() {
console.log("Count---componentWillMount")
}
// 组件已经挂载,常用,一般做一些初始化的事:例如开启定时器、发送网络请求
componentDidMount() {
console.log("Count---componentDidMount")
}
// 组件将要卸载,常用,一般做一些收尾工作,例如:关闭定时器、取消订阅消息
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("Count---componentWillUnmount")
}
// 组件是否应该更新,类似于阀门
shouldComponentUpdate() {
console.log("Count---shouldComponentUpdate")
return true
}
// 强制更新,不用经过阀门
forceUpdate() {
console.log("Count---forceUpdate")
}
// 组件将要更新
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log("Count---componentWillUpdate")
}
// 组件更新完毕
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log("Count---componentDidUpdate")
}
render() {
console.log("Count---render")
const { count } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2>当前求和为{count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.add}>点我+1</button>
<button onClick={this.death}>卸载组件</button>
<button onClick={this.force}>强制更新一下</button>
</div>
)
}
}
控制台执行
初始渲染打印
Count---constructor
Count---componentWillMount
Count---render
Count---componentDidMount
点击更新state打印
Count---shouldComponentUpdate
Count---componentWillUpdate
Count---render
Count---componentDidUpdate
强制更新打印
Count---forceUpdate
点击卸载打印
Count---componentWillUnmount
2、组件更新生命周期
class A extends React.Component {
state = { carName: '奔驰' }
changeCar = () => {
this.setState({ carName: '小米SU7' })
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>我是A组件</div>
<button onClick={this.changeCar}>换车</button>
<B carName={this.state.carName} />
</div>
)
}
}
class B extends React.Component {
// 组件将要接受新的props
componentWillReceiveProps(props) {
console.log("B---componentWillReceiveProps", props)
}
// 组件是否应该更新
shouldComponentUpdate() {
console.log("B---shouldComponentUpdate")
return true
}
// 组件将要更新
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log("B---componentWillUpdate")
}
// 组件更新完毕
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log("B---componentDidUpdate")
}
render() {
console.log("B---render")
const { carName } = this.props
return (
<div>
<div>我是B组件</div>
<div>当前车为:{carName}</div>
</div>
)
}
}
控制台输出
子组件初次渲染打印
B---render
电子更新父组件状态,子组件打印
B---componentWillReceiveProps
B---shouldComponentUpdate
B---componentWillUpdate
B---render
B---componentDidUpdate
# 生命周期流程图(新)
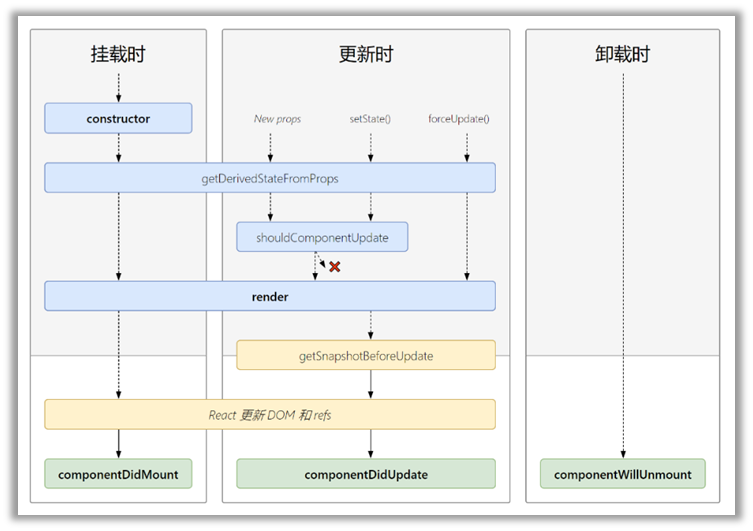
- getDerivedStateFromProps 如果state的值在任何时候都取决与props,可以使用
// 从props中派生出来的状态,必须是静态方法,且返回状态对象或null
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props) {
console.log("getDerivedStateFromProps")
return props
}
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 在更新之前获取快照,例如滚动位置
// 获取更新前的快照
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log("getSnapshotBeforeUpdate", prevProps, prevState)
// 返回值会传递给componentDidUpdate钩子
return 'huyadish'
}
# 重要的钩子
- render:初始化渲染或更新渲染调用
- componentDidMount:开启监听,发送ajax请求
- componentWillUnmount:做一些收尾工作,如清理定时器
# 即将废弃的钩子
- componentWillMount
- componentWillReceiveProps
- componentWillUpdate
在17版本使用会出现警告,在18版本必须加上UNSAFE_前缀才能使用,原因是React认为这三个钩子在未来的异步渲染会出现BUG
对比:新版本废弃了3个钩子,先添加了2个钩子
# 虚拟DOM和DOM diff算法
经典面试题:
react/vue中的key有什么作用?
当状态中数据发生变化时,react会根据新数据生成新的虚拟DOM,随后react会进行新旧虚拟DOM的diff比较,如果找到了相同的key
如果虚拟DOM内容没变,则使用之前的真实DOM,
如果内容变了,则生成新的真实DOM,随后替换掉页面中之前的真实DOM
如果没找到相同的key:根据数据创建新的真实DOM,随后渲染到页面
为什么遍历列表时,key最好不要用index?
- 若对数组进行逆序添加、逆序删除等破坏性操作,会产生没必要的DOM更新
- 如果结构中还包含输入类的DOM(如input),会产生错误DOM更新
- 如果仅用于渲染列表展示,使用index作为key是可以的
# React 脚手架 create-react-app
# create-react-app使用
全局安装脚手架命令
npm i -g create-react-app
将npm全局安装路径添加到环境变量path中
创建工程文件
create-react-app your-app-name
# index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<link rel="icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
<!--开启理想视口,用于做移动端网页适配-->
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<!--用于配置浏览器页签+地址栏颜色(仅支持安卓手机浏览器)-->
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
<meta
name="description"
content="Web site created using create-react-app"
/>
<!--用于指定网页添加到手机屏幕后的图标-->
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/logo192.png" />
<!--应用加壳时的配置文件-->
<link rel="manifest" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/manifest.json" />
<title>React App</title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>You need to enable JavaScript to run this app.</noscript>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
</html>
# 项目结构
- public 静态资源文件夹
- favicon.icon 网站页签标签
index.html 主页面- logo192.png logo图
- logo512.png logo图
- manifest.json 应用加壳配置文件
- robots.txt 爬虫协议文件
- src 源码文件夹
- App.css App组件的样式
- App.js App组件
- App.test.js 用于给App做测试
- index.css 样式
- index.js 入口文件
- logo.svg logo图
- reportWebVital.js 页面性能分析文件(需要web-vitals库的支持)
- setupTests.js 组件单元测试的文件(需要jest-dom库的支持)
# 样式的模块化
样式文件重命名,index.css——>index.module.css
模块化引入
import React,{Component} from "react";
import hello from './index.module.css'
export default class Index extends Component{
render() {
return (
<h2 className={hello.title}>Hello,React!</h2>
)
}
}
注意:使用css时可以考虑
# todoList案例相关知识点
- 拆分组件、实现静态组件,注意:className、style的写法
- 动态初始化列表,如何确定将数据放在哪个组件的state中?
- --某个组件使用,放在其自身的state中
- --某些组件使用,放在他们共同的父组件state中(官方称之为,状态提升)
- 关于父子组件通信:
- 父组件给子组件传递数据:通过props传递
- 子组件给父组件传递数据:通过props传递,要求父组件提前传递给子组件一个函数
- 注意
defaultChecked(首次生效)和checkd的区别?类似的还有defaultValue和value - 状态在哪里,操作状态的方法就在哪里
# react ajax代理
# 环境准备
- src/App.jsx
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import axios from "axios";
class App extends Component {
getStudentData = ()=>{
axios.get('http://localhost:3000/api1/students').then(
res=>{
console.log('成功了',res.data)
},
err=>{
console.log('失败了')
}
)
}
getCarData = ()=>{
axios.get('http://localhost:3000/api2/cars').then(
res=>{
console.log('成功了',res.data)
},
err=>{
console.log('失败了')
}
)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.getStudentData}>点我获取学生数据</button>
<button onClick={this.getCarData}>点我获取汽车数据</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
# http-proxy-middleware 代理配置
# v1.0.0+配置(最新版)
在src下创建配置文件:src/setupProxy.js
const { createProxyMiddleware } = require("http-proxy-middleware");
module.exports = function (app){
app.use('/api1', // 遇见/api1前缀的请求,就会触发该代理配置
createProxyMiddleware({
target: 'http://localhost:5000', // 请求转发给谁
changeOrigin: true, // 控制服务器收到的请求头中的Host字段的值
pathRewrite: {'^api1':''} // 重新请求路径(必须)
})
)
app.use('/api2',
createProxyMiddleware({
target: 'http://localhost:5001',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: {'^api2':''}
})
)
}
说明:
- 优点:可以配置多个代理,可以灵活的控制请求是否走代理。
- 缺点:配置繁琐,前端请求资源时必须加前缀。
# v0.21.0配置
const proxy = require('http-proxy-middleware')
module.exports = function(app) {
app.use(
proxy('/api1', { //api1是需要转发的请求(所有带有/api1前缀的请求都会转发给5000)
target: 'http://localhost:5000', //配置转发目标地址(能返回数据的服务器地址)
changeOrigin: true, //控制服务器接收到的请求头中host字段的值
pathRewrite: {'^/api1': ''} //去除请求前缀,保证交给后台服务器的是正常请求地址(必须配置)
}),
proxy('/api2', {
target: 'http://localhost:5001',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: {'^/api2': ''}
})
)
}
或者
在package.json中追加如下配置
"proxy":"http://localhost:5000"
说明:
- 优点:配置简单,前端请求资源时可以不加任何前缀。
- 缺点:不能配置多个代理。
- 工作方式:上述方式配置代理,当请求了3000不存在的资源时,那么该请求会转发给5000 (优先匹配前端资源)
# 跨域问题的本质
为什么
changeOrigin: true能解决跨域,它做了什么?答:而你的 API 服务器运行在
http://localhost:5000。当你的前端代码向/api发送请求时,代理中间件会将请求转发给http://localhost:5000。
- 如果没有
changeOrigin: true,API 服务器会看到请求来自http://localhost:3000。- 但是如果设置了
changeOrigin: true,API 服务器会认为请求是直接从http://localhost:5000发出的。
# Github接口测试
# 接口地址
github测试地址:https://api.github.com/search/users?q=keyword
可以根据用户名查询用户信息,如用户头像、主页地址等等,很好的mock数据
# 准备工作
项目结构
# 项目代码
- List/index.css
.album {
min-height: 50rem; /* Can be removed; just added for demo purposes */
padding-top: 3rem;
padding-bottom: 3rem;
background-color: #f7f7f7;
}
.card {
float: left;
width: 33.333%;
padding: .75rem;
margin-bottom: 2rem;
border: 1px solid #efefef;
text-align: center;
}
.card > img {
margin-bottom: .75rem;
border-radius: 100px;
}
.card-text {
font-size: 85%;
}
- List/index.jsx
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import "./index.css"
class List extends Component {
render() {
const {users,isFirst,isLoading,err} = this.props
return (
<div className="row">
{
isFirst ? <h2>欢迎使用,输入关键字,点击搜索</h2> :
isLoading ? <h2>Loading...</h2> :
err ? <h2 style={{color: "red"}}>{err}</h2> :
users.map(user=>{
return (
<div key={user.id} className="card">
<a rel="noreferrer" href={user.html_url} target="_blank">
<img alt="head_portrait" src={user.avatar_url}
style={{width: "100px"}}/>
</a>
<p className="card-text">{user.login}</p>
</div>
)
})
}
</div>
);
}
}
export default List;
- Search/index.jsx
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import axios from "axios";
class Search extends Component {
handleSearch = ()=>{
// 获取用户的输入(联系解构赋值+重命名)
const {keyWordNode: {value:keyword}} = this
// 发送请求前通知App更新状态
this.props.updateAppState({
isFirst: false,
isLoading: true
})
// 发送网络请求
axios.get(`https://api.github.com/search/users?q=${keyword}`).then(
response =>{
// 请求成功后通知app更新状态
this.props.updateAppState({
users: response.data.items,
isLoading: false
})
},
error=>{
// 请求失败了
this.props.updateAppState({
isLoading: false,
err: error.message
})
}
)
}
render() {
return (
<section className="jumbotron">
<h3 className="jumbotron-heading">搜索Github用户</h3>
<div>
<input ref={(c=>{this.keyWordNode = c})} type="text" placeholder="输入关键词点击搜索"/>
<button onClick={this.handleSearch}>搜索</button>
</div>
</section>
);
}
}
export default Search;
- App.js
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import "./components/List/index.css";
import Search from "./components/Search";
import List from "./components/List";
class App extends Component {
// 初始化状态
state = {
users: [], // 用户数据
isFirst: true, // 是否第一次打开页面
isLoading: false, // 是否处于加载中
err: "", // 存储请求相关的错误信息
}
// 更新app的state
updateAppState = (stateObj)=>{
this.setState(stateObj)
}
// 保存用户
saveUsers = (users)=>{
this.setState({users})
}
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<Search updateAppState={this.updateAppState}></Search>
<List {...this.state}></List>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
- index.js
// 引入react核心库
import React from "react";
// 引入reactDom
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
// 引入APP
import App from './App';
ReactDOM.render(<App/>,document.getElementById('root'));
效果预览:
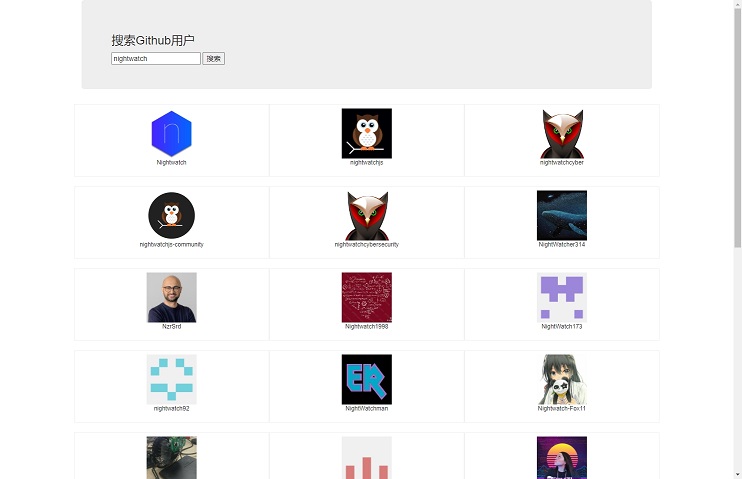
搜索框输入后,下方展示搜索结果中的用户头像,点击用户头像,会跳转到对应用户的主页
# 消息订阅与发布机制
# 安装PubSubJS
npm i -s pubsub-js
项目中引入
import PubSub from 'pubsub-js';
# 使用
- 订阅消息
// List组件中
componentDidMount() {
this.token = PubSub.subscribe("rong",(msg,data)=>{
this.setState(data)
})
}
componentWillUnmount(){
PubSub.unsubscribe(this.token)
}
- 发布消息
// 发送请求前通知List更新状态
PubSub.publish('rong',{isFirst:false,isLoading:true})
# Fetch
特点:
- 原生函数,不再使用XmlHttpRequest对象提交ajax请求
- 老版本浏览器可能不支持
Get请求:
fetch(url).then(function(response) {
return response.json()
}).then(function(data) {
console.log(data)
}).catch(function(e) {
console.log(e)
});
Post请求:
fetch(url, {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(data),
}).then(function(data) {
console.log(data)
}).catch(function(e) {
console.log(e)
})
# React路由
# 相关理解
# SPA的理解
- 单页面应用(single page web application,SPA)
- 整个应用只有一个完整的页面
- 点击页面中的链接不会刷新页面,只会做局部更新
- 数据都需要ajax请求,并在前端异步表现
# 路由的理解
锚点:在URL添加#和标识符,用于跳转到页面的指定位置,
history对象:浏览器的历史记录,由栈实现,跳转到新页面,或通过锚点跳转时,会在history栈顶添加一条数据,同时也支持直接通过api操作history对象。
使用
history.pushState和history.replaceState方法来改变 URL,而不会引起页面重新加载
前端路由:允许在不加载页面的情况下,更新URL并渲染不同的内容,有两种工作模式:
- 基于hash实现:兼容性好,支持一些比较老的浏览器
- 基于history实现:更为美观
# react-router-dom
# 简单使用
- 下载
npm install -s react-router-dom
- 引入
import {Link, Route} from 'react-router-dom'
- 导航区a标签改为Link
<Link className="list-group-item" to="/about">About</Link>
<Link className="list-group-item" to="/home">Home</Link>
- 展示区通过Route匹配路径
<Route path="/about" component={About}/>
<Route path="/home" component={Home}/>
- 最后在入口文件上App用
BrowserRouter或HashRouter包裹
// 引入router
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
ReactDOM.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<App/>
</BrowserRouter>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
# 组件分类
普通组件和路由组件区别:
- 写法不同:
- 一般组件:
<Header a={1}/> - 路由组件:
<Route path="/home" component={Home}/>
- 一般组件:
- 存放位置不同:
- 一般组件:components目录
- 路由组件:pages目录
- 路由组件会接收到三个props属性
- history
- location
- match
# 基本路由使用
# Navlink及其封装
- Navlink可以实现路由链接的高亮,通过activeClassName指定样式名
- 标签体内容是一个特殊的标签属性,通过this.props.children可以获取标签体内容
// 封装
class MyNavLink extends Component {
render() {
return (
<NavLink activeClassName="rong" className="list-group-item" {...this.props}/>
);
}
}
// 使用,标签体内容作为children属性,被props一并传递给NavLink
<MyNavLink to="/home">Home</MyNavLink>
# Switch
通常情况下,path和component是一一对应关系,Switch组件包裹的路由,在匹配到之后就不会继续向下匹配了**,可以提高路由匹配效率**。
<Switch>
<Route path="/about" component={About}/>
<Route path="/home" component={Home}/>
</Switch>
# 多级路径页面样式丢失
修改引入方式,public/index.html 中引入样式时:
不写
./写/(常用)不写
./写%PUBLIC_URL%(常用,React脚手架可用)
使用HashRouter
本质就是在请求css发起请求时,例如在
/a/b路径下获取,那么使用./时就会从当前路径也就是/a路径下去请求css,这时就会出错
# 模糊匹配
模糊匹配:跳转路径包含了注册路径,页面可以呈现,而且顺序要一致
<MyNavLink to="/home/b">Home</MyNavLink
<Route path="/home" component={Home}/>
严格匹配:注册路径必须和跳转路径一致,才能匹配到
<MyNavLink to="/home/b">Home</MyNavLink
<Route path="/home" exact component={Home}/>
注意:
严格匹配不要随便开启,有些时候开启会导致无法继续匹配二级路由
# 路由重定向
一般写在所有路由注册的最下方,当所有路由都无法匹配,跳转到Redirect指定的路由
<Switch>
<Route path="/about" component={About}/>
<Route path="/home" component={Home}/>
<Redirect to="/about"/>
</Switch>
# 嵌套路由
- 注册子路由时要写上父路由的path值
- 路由匹配是按照注册路由的顺序进行的,从父到子
父组件:
<div className="col-xs-2 col-xs-offset-2">
<div className="list-group">
{/*使用自己封装的导航栏*/}
<MyNavLink to="/about">About</MyNavLink>
<MyNavLink to="/home">Home</MyNavLink>
</div>
</div>
<div className="col-xs-6">
<div className="panel">
<div className="panel-body">
{/*注册路由*/}
<Switch>
<Route path="/about" component={About}/>
<Route path="/home" component={Home}/>
<Redirect to="/about"/>
</Switch>
</div>
</div>
</div>
子组件:
<ul className="nav nav-tabs">
<li>
<MyNavLink to="/home/news">News</MyNavLink>
</li>
<li>
<MyNavLink to="/home/message">Message</MyNavLink>
</li>
</ul>
<Switch>
<Route path="/home/news" component={News}/>
<Route path="/home/message" component={Message}/>
<Redirect to="/home/news"/>
</Switch>
# 路由传参
# params参数
- 声明传递
{/*向路由组件传递params参数*/}
<Link to={`/home/message/detail/${msgObj.id}/${msgObj.title}`}>{msgObj.title}</Link>
- 声明接收
{/*声明接受params参数*/}
<Route path="/home/message/detail/:id/:title" component={Detail}/>
- 使用参数
const {id, title} = this.props.match.params
# search参数
- 声明传递
{/*向路由组件传递search参数*/}
<Link to={`/home/message/detail/?id=${msgObj.id}&title=${msgObj.title}`}>{msgObj.title}</Link>
- 声明接受
{/*无需声明接受search参数*/}
<Route path="/home/message/detail" component={Detail}/>
- 使用参数
// 接收search参数
const {search} = this.props.location
const {id,title} = qs.parse(search.slice(1))
注意:
- react17版本内置了querystring库
- react18版本需要手动安装
npm i -s qs- 形如
'carName=奔驰&price=199'格式的字符串称为urlencoded字符串
# state参数
- 声明传递
{/*向路由组件传递state参数*/}
<Link to={{pathname:"/home/message/detail",state:{id:msgObj.id,title:msgObj.title}}}>{msgObj.title}</Link>
- 声明接受
{/*无需声明接受search参数*/}
<Route path="/home/message/detail" component={Detail}/>
- 使用参数
const {id,title} = this.props.location.state || {}
# 小结
使用场景
- params参数是使用最多的
- state参数可以在地址栏隐藏用户信息,同时注意路由不会改变,不会压入history
# 路由跳转
<Link replace to={{pathname:"/home/message/detail",state:{id:msgObj.id,title:msgObj.title}}}>{msgObj.title}</Link>
路由组件上添加replace属性开启该路由的replace模式
# 编程式路由导航
调用当前组件的this.props.history上的replace、push方法,同时支持三种模式
所有的路由组件会共享一个this.props.history,并且由react-router管理
// 跳转到detail,并且为replace跳转
replaceShow = (id,title)=>{
// replace跳转+params参数
// this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detail/${id}/${title}`)
// replace跳转+search参数
// this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detail/?id=${id}&title=${title}`)
// replace跳转+state参数
this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detail`,{id,title})
}
pushShow = (id,title)=>{
// push跳转+params参数
// this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detail/${id}/${title}`)
// push跳转+search参数
// this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detail/?id=${id}&title=${title}`)
// push跳转+state参数
this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detail`,{id,title})
}
// 后退
back = () => {
this.props.history.goBack()
}
// 前进
forward = () => {
this.props.history.goForward()
}
// 跳转n位
go = () => {
this.props.history.go(-2)
}
# withRouter的使用
import withRouter from "react-router-dom/es/withRouter";
...
export default withRouter(Header);
withRouter可以加工一般组件,让一般组件拥有路由组件特有的API:location、match、history
# 路由模式
- BrowserRouter没有任何影响,因为state保存在history对象中
- HashRouter刷新后会导致路由state参数丢失!!!
注意:浏览器刷新会清空内存并初始化页面
# React-UI组件库
antd
# Redux
# redux理解
- redux是什么
- 专门用于做状态管理的库
- 可以用在react、angular、vue等项目中
- 集中式管理react应用中多个组件共享的状态
- 什么情况下需要使用redux
- 某个组件的状态,需要让其他组件可以随时拿到
- 一个组件需要改变另一个组件的状态
- 总体原则:能不用就不用,如果不用比较吃力才考虑使用
# redux的三个核心概念
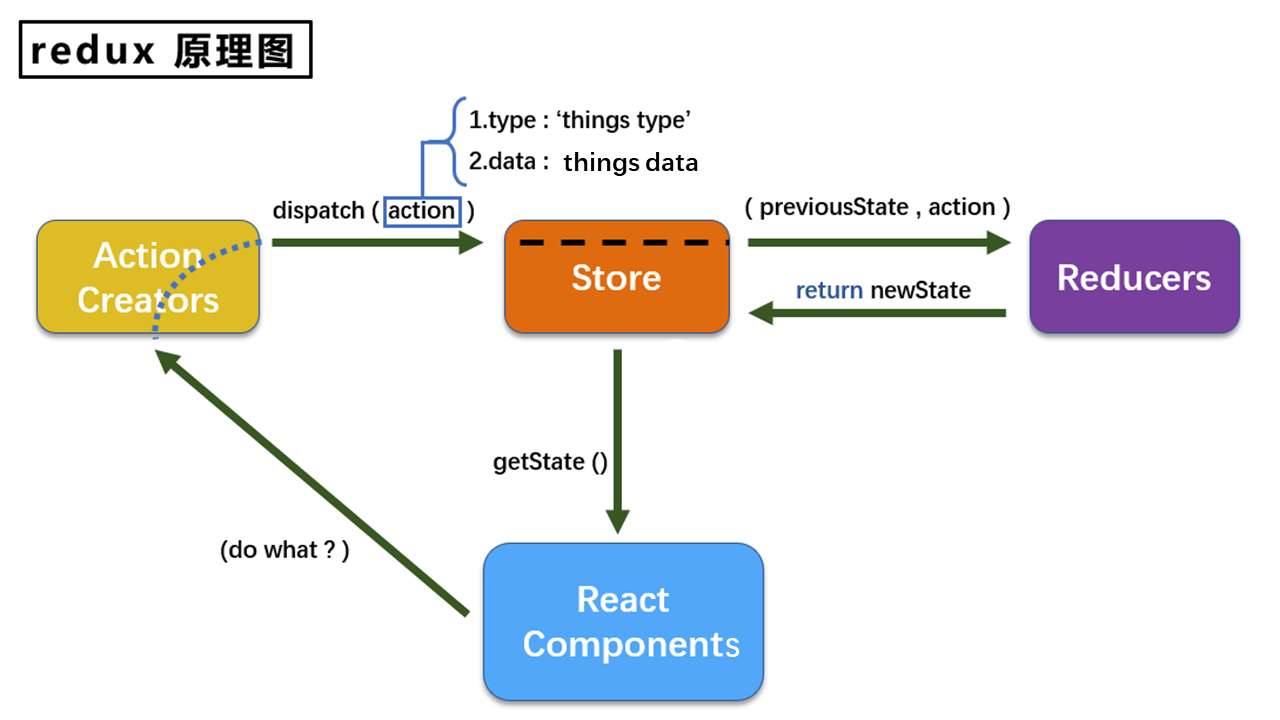
# action
action是动作的对象,包含两个属性:
- type:标识属性,值为字符串,唯一,必要属性
- data:数据属性,值类型任意,可选属性
例如:{type:"ADD_STUDENT",data:{name:"tom",age:18}}
# reducer
- 用于初始化状态、加工状态。
- 加工时,根据旧的state和action,产生新的state的,并且是一个纯函数。
# store
思考:三者的关系
- component类似于要去吃饭的客人,客人可以点菜
- Action creators类似于服务员,把客人点菜的清单交给前台
- Store类似于前台,接受服务员拿来的菜单,同时通知后厨做菜
- Reducer类似于厨师,收到做菜的清单,返回菜品
# redux的核心API
createStore: 创建包含指定reducer的store对象
store对象: redux库最核心的管理对象,内部维护着:
- state
- reducer
applyMiddleware: 使用基于redux的中间件
combineReducers: 合并多个reducer函数
// 引入createStore,专门用于创建redux中最为核心的store对象
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
// 引入为Count组件服务的reducer
import countReducer from './count_reducer'
// 引入redux-thunk,用于支持异步action
import {thunk} from 'redux-thunk'
// 暴露store
export default createStore(
countReducer,
applyMiddleware(thunk)
)
使用store
import store from '../../redux/store'
// 获取state
render(){
return (
<h1>当前求和为:{store.getState()}</h1>
)
}
// 提交action
increment = ()=>{
const {value} = this.selectNumber
store.dispatch(createIncrementAction(value*1))
}
// 监听store中state变化
componentDidMount() {
// 监测redux中状态的变化,只要变化,就调用render
store.subscribe(()=>{
// 调用render 不够优雅
this.setState({})
})
}
# redux异步编程
安装中间件
npm i -s redux-thunk
redux默认不能进行异步处理,某些时候应用需要在redux执行异步任务(ajax,定时器)
# react-redux
# 介绍
一个react插件库,专门用来简化在react中使用redux
react-redux将所有组件分为两大类:
- UI组件:
- 只负责UI的呈现,不带有任何业务逻辑
- 通过props接受数据
- 不使用任何redux的api
- 一般保存在components目录下
- 容器组件:
- 负责管理数据和业务逻辑,不负责UI的呈现
- 使用redux的API
- 一般保存在containers目录下
# 基本使用
定义一个Count容器组件
// 引入Count的UI组件
import CountUI from '../../components/Count'
// 引入connect用于连接UI组件与redux
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
import { createIncrementAction,
createDecrementAction,
createIncrementAsyncAction} from "../../redux/count_creator";
// mapStateToProps 函数返回的对象作为状态 通过props传递给UI组件
function mapStateToProps(state){
return { count: state }
}
// mapDispatchToProps 函数返回的对象作为操作状态的方法 通过props传递给UI组件
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch){
return {
add: number => dispatch(createIncrementAction(number)),
minus: number => dispatch(createDecrementAction(number)),
jiaAsync: (number,time) => dispatch(createIncrementAsyncAction(number,time)),
}
}
// 创建并暴露一个容器组件
export default connect(mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToProps)(CountUI)
在App.jsx引入,通过标签属性传递store对象
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import Count from "./containers/Count";
import store from "./redux/store"
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
{/*给容器组件传递容器组件*/}
<Count store={store}></Count>
</div>
);
}
}
# 简写形式
// 创建并暴露一个容器组件
export default connect(
state => ({ count: state }),
// mapDispatchToProps一般写法
// dispatch => ({
// add: number => dispatch(createIncrementAction(number)),
// minus: number => dispatch(createDecrementAction(number)),
// jiaAsync: (number,time) => dispatch(createIncrementAsyncAction(number,time)),
// })
// mapDispatchToProps简写形式
{
add: createIncrementAction,
minus: createDecrementAction,
jiaAsync: createIncrementAsyncAction
}
)(CountUI)
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
import store from "./redux/store"
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<App/>)
// 使用了react-redux,这一步也不需要了
// store.subscribe(()=>{
// root.render(<App/>)
// })
# 小结
react-redux作用:
- 无需自己监测store的变化,再调用render函数,容器组件可以自动完成
- 可以使用
<Provider/>统一为所有的组件传递store - 核心就是通过connect函数连接UI组件,和Store,并返回容器组件
- 容器组件和UI组件可以整合成一个文件
- mapDispatchToProps
# 使用redux调试工具
安装
npm i -s @redux-devtools/extension
引入
// 引入@redux-devtools/extension
import { composeWithDevTools } from '@redux-devtools/extension'
// 暴露store
export default createStore(
reducers,
composeWithDevTools(
applyMiddleware(...middleware)
)
)
浏览器应用商店安装Redux Devtools
# 纯函数
纯函数是一类特别的函数:只要是同样的输入,必定得到同样的输出
必须遵守以下约束:
- 不得改写参数数据
- 不会产生任何副作用,例如网络请求,输入和输出设备
- 不能调用Date.now()或Math.random()等不纯的方法
redux的reducer函数必须是一个纯函数
# 扩展
# setState
对象式用法
// 1. 获取当前state中的count值
const {count} = this.state;
// 2. 更新代码
this.setState({count: count + 1}, () => {
// react状态更新是异步的,改完了状态可以在回调中查看
console.log(this.state.count);
});
函数式用法
this.setState(state => ({count: state.count + 1}));
区别:
- 如果新状态不依赖与原状态,可以使用对象方式
- 如果新状态依赖于原状态,使用函数方式
- 如果需要在setState执行后获取最新数据,可以在第二个callback函数中获取
# lazyLoad
路由组件懒加载,配合Suspense使用
//1.通过React的lazy函数配合import()函数动态加载路由组件 ===> 路由组件代码会被分开打包
const Login = lazy(()=>import('@/pages/Login'))
//2.通过<Suspense>指定在加载得到路由打包文件前显示一个自定义loading界面
<Suspense fallback={<h1>loading.....</h1>}>
<Switch>
<Route path="/xxx" component={Xxxx}/>
<Redirect to="/login"/>
</Switch>
</Suspense>
# Hooks
# React Hooks是什么?
- Hook是React 16.8.0版本增加的新特性/新语法
- 可以让你在函数组件中使用 state 以及其他的 React 特性
# 三个常用的Hook
- State Hook: React.useState()
- Effect Hook: React.useEffect()
- Ref Hook: React.useRef()
# State Hook
State Hook让函数组件也可以有state状态, 并进行状态数据的读写操作 语法:
const [xxx, setXxx] = React.useState(initValue)
useState()说明:
参数: 第一次初始化指定的值在内部作缓存
返回值: 包含2个元素的数组, 第1个为内部当前状态值, 第2个为更新状态值的函数
setXxx()2种写法:
setXxx(newValue): 参数为非函数值, 直接指定新的状态值, 内部用其覆盖原来的状态值
setXxx(value => newValue): 参数为函数, 接收原本的状态值, 返回新的状态值, 内部用其覆盖原来的状态值
import React, {Component, useState} from 'react';
function Demo() {
// react底层做了处理,这里只会调用一次
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const [name, setName] = useState('rong');
function add() {
// setCount(count + 1); // 第一种写法
setCount(count => count + 1); // 第二种写法
// 和setState一样
}
function changeName() {
setName('rong2');
}
return (
<div>
<h2>当前求和为:{count}</h2>
<h2>我的名字是:{name}</h2>
<button onClick={add}>点我+1</button>
<button onClick={changeName}>点我改名</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Demo;
# Effect Hook
Effect Hook可以在函数式组件中执行副作用操作,用于模拟组件的生命周期钩子
useEffect函数需要两个参数:
- 第一个参数是回调函数,当依赖项发生变化时回调函数会执行
- 第二个参数是依赖项,如组件的的state
常见用法:
- 等价于componentDidMount
// 第二个参数为[]
React.useEffect(() => {
// 此时函数体相当于componentDidMount
setInterval(() => {
setCount(count => count + 1);
}, 1000);
}, []);
- 等价于componentDidMount + componentDidUpdate
// 第二个参数为依赖项,当依赖项发生变化时,函数体才会执行
React.useEffect(() => {
// 此时函数体相当于componentDidMount + componentDidUpdate
console.log(count);
}, [count]);
- 等价于componentWillUnmount
React.useEffect(() => {
let timer = setInterval(() => {
setCount(count => count + 1);
}, 1000);
// 等价于componentWillUnmount
return () => {
clearInterval(timer);
};
}, []);
# Ref Hook
Ref Hook可以在函数组件中存储/查找组件内标签或任意其他数据
语法:
const myRef = React.useRef();
使用:
<input type="text" ref={myRef}/>
<button onClick={()=>{alert(myRef.current.value)}}>点击提示</button>
# Fragment
当我们的租金返回值,根目录有多个标签的时候,需要用div包裹。但是浏览器解析的时候会多一个没用的div
class Demo extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<input type="text"/>
</div>
);
}
}
使用Fragment作为根标签,react解析后不会生成多余的div标签
import React, {Component, Fragment} from 'react';
class Demo extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
</Fragment>
);
}
}
也可以使用:
class Demo extends Component {
render() {
return (
<>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<input type="text"/>
</>
);
}
}
区别:
- Fragment标签作为组件根标签,只能接收一个key属性,用于遍历
- <></>空标签不能写任何属性
# Context
一种组件通信方式,常用于祖组件和后代组件的通信
# 基本使用
A-B-C为三层嵌套关系
- A组件
import React, {Component} from 'react';
const MyContext = React.createContext();
const { Provider } = MyContext;
export default class A extends Component {
state = {
username: 'Tom'
}
render() {
const { username } = this.state;
return (
<div className="parent">
<h3>我是A组件</h3>
<h4>我的用户名是:{username}</h4>
<Provider value={{username}}>
<B/>
</Provider>
</div>
);
}
}
- B组件
class B extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div className="child">
<h3>我是b组件</h3>
<C/>
</div>
);
}
}
- C组件类式写法
// C组件类式写法
class C extends Component {
// 接收context需要手动声明
static contextType = MyContext;
render() {
return (
<div className="grand">
<h3>我是C组件</h3>
<h4>我的从A接收到的用户名是:{this.context.username}</h4>
</div>
);
}
}
- C组件函数式写法
function C() {
// 接收context不需要手动声明
const context = React.useContext(MyContext);
return (
<div className="grand">
<h3>我是C组件</h3>
<h4>我的从A接收到的用户名是:{context.username}</h4>
</div>
)
}
注意:函数式组件也不要用Consumer,太不优雅了
# 组件优化
Component的2个问题 :
只要执行setState(),即使不改变状态数据, 组件也会重新render() ==> 效率低
只当前组件重新render(), 就会自动重新render子组件,纵使子组件没有用到父组件的任何数据 ==> 效率低
效率高的的做法:
- 只有当组件的state或props数据发生改变时才重新render()
原因:
- Component中的shouldComponentUpdate()总是返回true
解决办法:
办法1: 重写
shouldComponentUpdate()方法 比较新旧state或props数据, 如果有变化才返回true, 如果没有返回false 办法2:
使用PureComponentPureComponent重写了shouldComponentUpdate(), 只有state或props数据有变化才返回true 注意: 只是进行state和props数据的浅比较, 如果只是数据对象内部数据变了, 返回false
不要直接修改state数据, 而是要产生新数据 项目中一般使用PureComponent来优化
示例代码:
父组件
export default class Parent extends PureComponent {
state = { carName: '宝马' }
changeCar = () => {
// 使用PureComponent时,要产生新数据
this.setState({carName: '奥迪'});
}
// shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) {
// // 状态没有变化不会调用render
// return this.state.carName !== nextState.carName;
// }
render() {
console.log("Parent render")
const { carName } = this.state;
return (
<div className="parent">
<h3>我是Parent组件</h3>
<span>我的车名字是: {carName}</span>
<button onClick={this.changeCar}>点我换车</button>
<Child carName={carName}/>
</div>
);
}
};
子组件
class Child extends PureComponent {
// shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) {
// return this.props.carName !== nextProps.carName;
// }
render() {
console.log("Child render")
return (
<div className="child">
<h3>我是Child组件</h3>
<span>我接到的车:{this.props.carName}</span>
</div>
);
}
};
# render props
如何向组件内部动态传入带内容的结构,同时还要传递数据?
Vue中: 使用插槽技术
React中:
- 使用children props: 通过组件标签体传入结构
- 使用render props: 通过组件标签属性传入结构,一般用render函数属性
childern props:
// A组件的父组件中
<A>
<B>xxx</B>
</A>
// A组件中
{this.props.children}
render props:
// A组件的父组件
<A render={(name)=><B name={name}/>}/>
// A组件中,传入state数据
{this.props.render(name)}
// B组件中,读取传入的state
{this.props.name}
# 错误边界
错误边界:用来捕获后代组件错误,渲染出备用页面
特点:只能捕获后代组件生命周期产生的错误,不能捕获自己组件产生的错误和其他组件在合成事件、定时器中产生的错误
使用方式:
class Parent extends Component {
state = {
hasError: false,
};
// 当Parent的子组件发生错误的时候,会执行这个方法,并携带错误信息
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
console.log(error)
// render之前触发
// 返回新的state
return {hasError: true};
}
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
// 统计页面的错误,发送请求到后台
console.log(error, info)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>我是Parent组件</h2>
{this.state.hasError ? (
<div>
<h4>当前网络不稳定,稍后再试</h4>
</div>
) : (
<Child />
)}
</div>
);
}
}
# 组件通信方式总结
几种通信方式:
- props:
- children props
- render props
- 消息订阅与发布:pubsub.js、event等
- 集中式管理:redux、dva(轻量状态管理)等
- conText:生产者-消费者模式
比较好的搭配方式:
父子组件:props
兄弟组件:消息订阅——发布、集中式管理
祖孙组件:消息订阅——发布、集中式管理、conText(开发用的少,封装插件用的多)
# React Router6
# 概述
React Router 以三个不同的包发布到 npm 上,它们分别为:
- react-router: 路由的核心库,提供了很多的:组件、钩子。
- react-router-dom: 包含react-router所有内容,并添加一些专门用于 DOM 的组件,例如
<BrowserRouter>等 。 - react-router-native: 包括react-router所有内容,并添加一些专门用于ReactNative的API,例如:
<NativeRouter>等。
与React Router 5.x 版本相比,改变了什么?
内置组件的变化:移除
<Switch/>,新增<Routes/>等。语法的变化:
component={About}变为element={<About/>}等。新增多个hook:
useParams、useNavigate、useMatch等。官方明确推荐函数式组件了!!!
......
# Component
# <BrowserRouter>
说明:
<BrowserRouter>用于包裹整个应用。示例代码:
import React from "react"; import ReactDOM from "react-dom"; import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom"; ReactDOM.render( <BrowserRouter> {/* 整体结构(通常为App组件) */} </BrowserRouter>,root );
# <HashRouter>
- 说明:作用与
<BrowserRouter>一样,但<HashRouter>修改的是地址栏的hash值。 - 备注:6.x版本中
<HashRouter>、<BrowserRouter>的用法与 5.x 相同。
# <Routes/> 与 <Route/>
v6版本中移出了先前的
<Switch>,引入了新的替代者:<Routes>。<Routes>和<Route>要配合使用,且必须要用<Routes>包裹<Route>。<Route>相当于一个 if 语句,如果其路径与当前 URL 匹配,则呈现其对应的组件。<Route caseSensitive>属性用于指定:匹配时是否区分大小写(默认为 false)。当URL发生变化时,
<Routes>都会查看其所有子<Route>元素以找到最佳匹配并呈现组件 。<Route>也可以嵌套使用,且可配合useRoutes()配置 “路由表” ,但需要通过<Outlet>组件来渲染其子路由。示例代码:
<Routes> /*path属性用于定义路径,element属性用于定义当前路径所对应的组件*/ <Route path="/login" element={<Login />}></Route> /*用于定义嵌套路由,home是一级路由,对应的路径/home*/ <Route path="home" element={<Home />}> /*test1 和 test2 是二级路由,对应的路径是/home/test1 或 /home/test2*/ <Route path="test1" element={<Test/>}></Route> <Route path="test2" element={<Test2/>}></Route> </Route> //Route也可以不写element属性, 这时就是用于展示嵌套的路由 .所对应的路径是/users/xxx <Route path="users"> <Route path="xxx" element={<Demo />} /> </Route> </Routes>
# <Link>
作用: 修改URL,且不发送网络请求(路由链接)。
注意: 外侧需要用
<BrowserRouter>或<HashRouter>包裹。示例代码:
import { Link } from "react-router-dom"; function Test() { return ( <div> <Link to="/路径">按钮</Link> </div> ); }
# <NavLink>
作用: 与
<Link>组件类似,且可实现导航的“高亮”效果。示例代码:
// 注意: NavLink默认类名是active,下面是指定自定义的class //自定义样式 <NavLink to="login" className={({ isActive }) => { console.log('home', isActive) return isActive ? 'base one' : 'base' }} >login</NavLink> /* 默认情况下,当Home的子组件匹配成功,Home的导航也会高亮, 当NavLink上添加了end属性后,若Home的子组件匹配成功,则Home的导航没有高亮效果。 */ <NavLink to="home" end >home</NavLink>
# <Navigate>
作用:只要
<Navigate>组件被渲染,就会修改路径,切换视图。replace属性用于控制跳转模式(push 或 replace,默认是push)。示例代码:
import React,{useState} from 'react' import {Navigate} from 'react-router-dom' export default function Home() { const [sum,setSum] = useState(1) return ( <div> <h3>我是Home的内容</h3> {/* 根据sum的值决定是否切换视图 */} {sum === 1 ? <h4>sum的值为{sum}</h4> : <Navigate to="/about" replace={true}/>} <button onClick={()=>setSum(2)}>点我将sum变为2</button> </div> ) }
# <Outlet>
当
<Route>产生嵌套时,渲染其对应的后续子路由。示例代码:
//根据路由表生成对应的路由规则 const element = useRoutes([ { path:'/about', element:<About/> }, { path:'/home', element:<Home/>, children:[ { path:'news', element:<News/> }, { path:'message', element:<Message/>, } ] } ]) //Home.js import React from 'react' import {NavLink,Outlet} from 'react-router-dom' export default function Home() { return ( <div> <h2>Home组件内容</h2> <div> <ul className="nav nav-tabs"> <li> <NavLink className="list-group-item" to="news">News</NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink className="list-group-item" to="message">Message</NavLink> </li> </ul> {/* 指定路由组件呈现的位置 */} <Outlet /> </div> </div> ) }
# Hooks
# useRoutes()
作用:根据路由表,动态创建
<Routes>和<Route>。示例代码:
//路由表配置:src/routes/index.js import About from '../pages/About' import Home from '../pages/Home' import {Navigate} from 'react-router-dom' export default [ { path:'/about', element:<About/> }, { path:'/home', element:<Home/> }, { path:'/', element:<Navigate to="/about"/> } ] //App.jsx import React from 'react' import {NavLink,useRoutes} from 'react-router-dom' import routes from './routes' export default function App() { //根据路由表生成对应的路由规则 const element = useRoutes(routes) return ( <div> ...... {/* 注册路由 */} {element} ...... </div> ) }
# useNavigate()
作用:返回一个函数用来实现编程式导航。
示例代码:
import React from 'react' import {useNavigate} from 'react-router-dom' export default function Demo() { const navigate = useNavigate() const handle = () => { //第一种使用方式:指定具体的路径 navigate('/login', { replace: false, state: {a:1, b:2} }) //第二种使用方式:传入数值进行前进或后退,类似于5.x中的 history.go()方法 navigate(-1) } return ( <div> <button onClick={handle}>按钮</button> </div> ) }
# useParams()
作用:回当前匹配路由的
params参数,类似于5.x中的match.params。示例代码:
import React from 'react'; import { Routes, Route, useParams } from 'react-router-dom'; import User from './pages/User.jsx' function ProfilePage() { // 获取URL中携带过来的params参数 let { id } = useParams(); } function App() { return ( <Routes> <Route path="users/:id" element={<User />}/> </Routes> ); }
# useSearchParams()
作用:用于读取和修改当前位置的 URL 中的查询字符串。
返回一个包含两个值的数组,内容分别为:当前的seaech参数、更新search的函数。
示例代码:
import React from 'react' import {useSearchParams} from 'react-router-dom' export default function Detail() { const [search,setSearch] = useSearchParams() const id = search.get('id') const title = search.get('title') const content = search.get('content') return ( <ul> <li> <button onClick={()=>setSearch('id=008&title=哈哈&content=嘻嘻')}>点我更新一下收到的search参数</button> </li> <li>消息编号:{id}</li> <li>消息标题:{title}</li> <li>消息内容:{content}</li> </ul> ) }
# useLocation()
作用:获取当前 location 信息,对标5.x中的路由组件的
location属性。示例代码:
import React from 'react' import {useLocation} from 'react-router-dom' export default function Detail() { const x = useLocation() console.log('@',x) // x就是location对象: /* { hash: "", key: "ah9nv6sz", pathname: "/login", search: "?name=zs&age=18", state: {a: 1, b: 2} } */ return ( <ul> <li>消息编号:{id}</li> <li>消息标题:{title}</li> <li>消息内容:{content}</li> </ul> ) }
# useMatch()
作用:返回当前匹配信息,对标5.x中的路由组件的
match属性。示例代码:
<Route path="/login/:page/:pageSize" element={<Login />}/> <NavLink to="/login/1/10">登录</NavLink> export default function Login() { const match = useMatch('/login/:x/:y') console.log(match) //输出match对象 //match对象内容如下: /* { params: {x: '1', y: '10'} pathname: "/LoGin/1/10" pathnameBase: "/LoGin/1/10" pattern: { path: '/login/:x/:y', caseSensitive: false, end: false } } */ return ( <div> <h1>Login</h1> </div> ) }
# useInRouterContext()
作用:如果组件在 <Router> 的上下文中呈现,则 useInRouterContext 钩子返回 true,否则返回 false。
# useNavigationType()
- 作用:返回当前的导航类型(用户是如何来到当前页面的)。
- 返回值:
POP、PUSH、REPLACE。 - 备注:
POP是指在浏览器中直接打开了这个路由组件(刷新页面)。
# useOutlet()
作用:用来呈现当前组件中渲染的嵌套路由。
示例代码:
const result = useOutlet() console.log(result) // 如果嵌套路由没有挂载,则result为null // 如果嵌套路由已经挂载,则展示嵌套的路由对象
# useResolvedPath()
- 作用:给定一个 URL值,解析其中的:path、search、hash值。